Introduction
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that affects the mesothelium, a protective lining covering the internal organs. It is primarily caused by exposure to asbestos fibers. One crucial aspect of understanding mesothelioma is knowing the stages of the disease and how it progresses. In this article, we will delve into the mesothelioma stages, providing a detailed overview of each stage, including symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and prognosis.
Mesothelioma Stages
The mesothelioma stages are used to describe the extent and progression of the disease. The staging system helps medical professionals determine the appropriate treatment plan and predict the patient’s prognosis. There are different staging systems used for mesothelioma, including the Butchart, TNM, and Brigham systems. The following sections will provide an in-depth look at each stage.
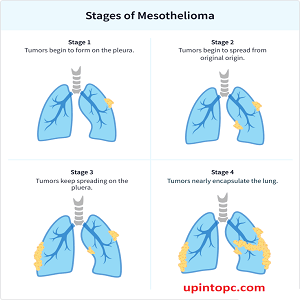
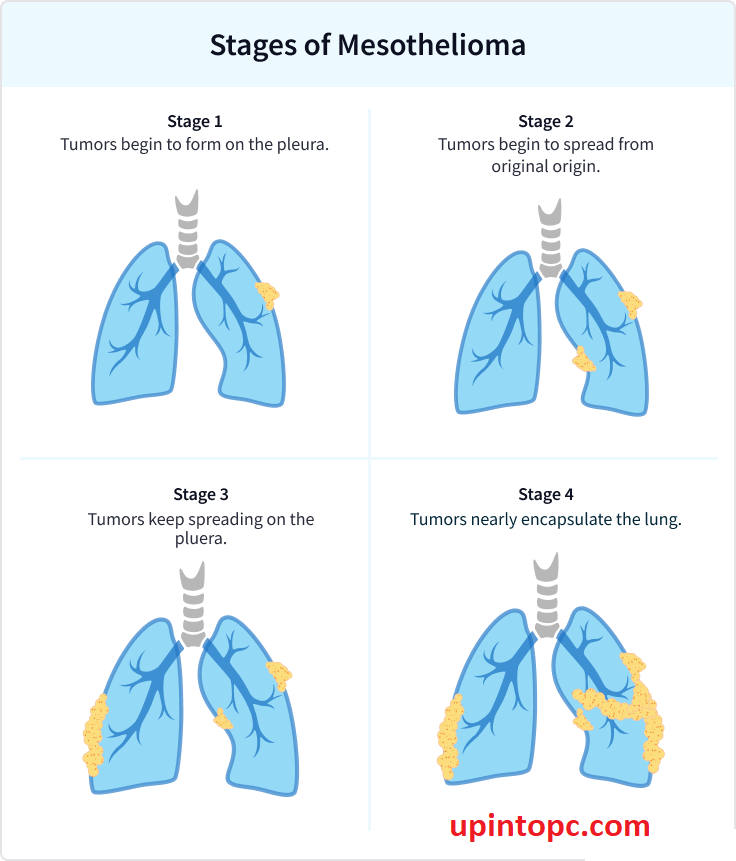
Stage 1: Localized Mesothelioma
At stage 1, mesothelioma is still localized, meaning it has not spread beyond the initial site of origin. Commonly, it affects the lining of one lung (pleural mesothelioma), but it can also develop in the lining of the abdomen (peritoneal mesothelioma) or heart (pericardial mesothelioma). In this early stage, treatment options are more varied, and the prognosis is generally better.
Symptoms
- Persistent cough
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
Diagnostic Methods
- Chest X-ray
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- PET scan
- Biopsy
Treatment Options
- Surgery: Options include pleurectomy/decortication (P/D) or extrapleural pneumonectomy (EPP).
- Radiation therapy: High-energy rays are used to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Powerful drugs are administered to destroy cancer cells.
Prognosis
The prognosis for stage 1 mesothelioma is generally more favorable compared to later stages. With early detection and appropriate treatment, the median survival rate can range from 21 to 50 months, depending on various factors such as overall health and the specific subtype of mesothelioma.
Stage 2: Advanced Localized Mesothelioma
Stage 2 mesothelioma is characterized by a more advanced tumor growth that may have spread to nearby structures and lymph nodes. The cancer is still considered localized, but the treatment options become more limited as the disease progresses.
Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Sweating and fever
Diagnostic Methods
- Imaging tests: CT scan, MRI scan, PET scan
- Biopsy
Treatment Options
- Surgery: Depending on the extent of tumor growth, surgical options may include P/D or EPP.
- Radiation therapy: Used to relieve symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease.
- Chemotherapy: Administered to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.
Prognosis
The prognosis for stage 2 mesothelioma is relatively better than later stages. The median survival rate ranges from 19 to 38 months, depending on various factors such as the patient’s overall health, age, and response to treatment.
Stage 3: Regional Spread
Stage 3 mesothelioma signifies that the cancer has spread extensively within the original region and possibly to nearby lymph nodes. Treatment becomes more challenging at this stage, and the goal shifts to managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Chronic cough with blood
- Difficulty swallowing
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
Diagnostic Methods
- Imaging tests: CT scan, MRI scan, PET scan
- Biopsy
Treatment Options
- Surgery: In some cases, palliative procedures may be performed to relieve symptoms, but curative surgery is generally not an option.
- Radiation therapy: Used to alleviate pain and control tumor growth.
- Chemotherapy: Administered to slow down the progression of the disease and improve quality of life.
Prognosis
The prognosis for stage 3 mesothelioma is poorer compared to earlier stages. The median survival rate ranges from 12 to 24 months, depending on various factors such as the patient’s overall health, age, and response to treatment.
Stage 4: Distant Metastasis
Stage 4 mesothelioma is the most advanced stage, where the cancer has spread extensively to distant organs and tissues throughout the body. At this stage, treatment options are focused on palliative care to alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Symptoms
- Severe chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty swallowing
- Persistent cough with blood
- Severe weight loss
Diagnostic Methods
- Imaging tests: CT scan, MRI scan, PET scan
- Biopsy
Treatment Options
- Palliative care: Focuses on managing symptoms, relieving pain, and improving quality of life.
- Radiation therapy: Used to alleviate pain and control tumor growth.
- Chemotherapy: Administered to slow down the progression of the disease and manage symptoms.
Prognosis
The prognosis for stage 4 mesothelioma is the least favorable. The median survival rate ranges from 6 to 12 months, depending on various factors such as the patient’s overall health, age, and response to palliative treatments.
FAQs about Mesothelioma Stages
- What are the risk factors for developing mesothelioma?
- Asbestos exposure is the primary risk factor for developing mesothelioma. Other factors may include genetics, age, and certain occupations.
- How mesothelioma can diagnose?
- Mesothelioma can diagnose through a combination of imaging tests. Such as CT scans and biopsies, where a tissue sample taken for examination.
- Can mesothelioma cure?
- While there is currently no known cure for mesothelioma, early detection, and treatment can significantly improve a patient’s prognosis and quality of life.
- Are there any alternative therapies for mesothelioma?
- Complementary therapies such as acupuncture, massage, and meditation may help manage symptoms and improve well-being, but they cannot consider curative treatments.
- Mesothelioma caused by asbestos exposure?
- Asbestos exposure is the primary cause of mesothelioma, but there have been rare cases where the disease occurred without a known asbestos exposure history.
- Can mesothelioma prevent?
- Mesothelioma can prevent avoiding asbestos exposure. Strict regulations and safety measures in industries where asbestos is present are crucial in preventing the disease.
Conclusion
Understanding the stages of mesothelioma is essential for patients, their families, and medical professionals. The progression of the disease influences treatment options, prognosis, and quality of life. By recognizing the symptoms, undergoing early detection methods, and exploring appropriate treatment strategies, patients can have a better chance of managing the disease effectively. With ongoing research and advancements in medical science, there is hope for improved treatment outcomes and increased survival rates for mesothelioma patients.